HOW DOES A HYBRID CAR WORK?
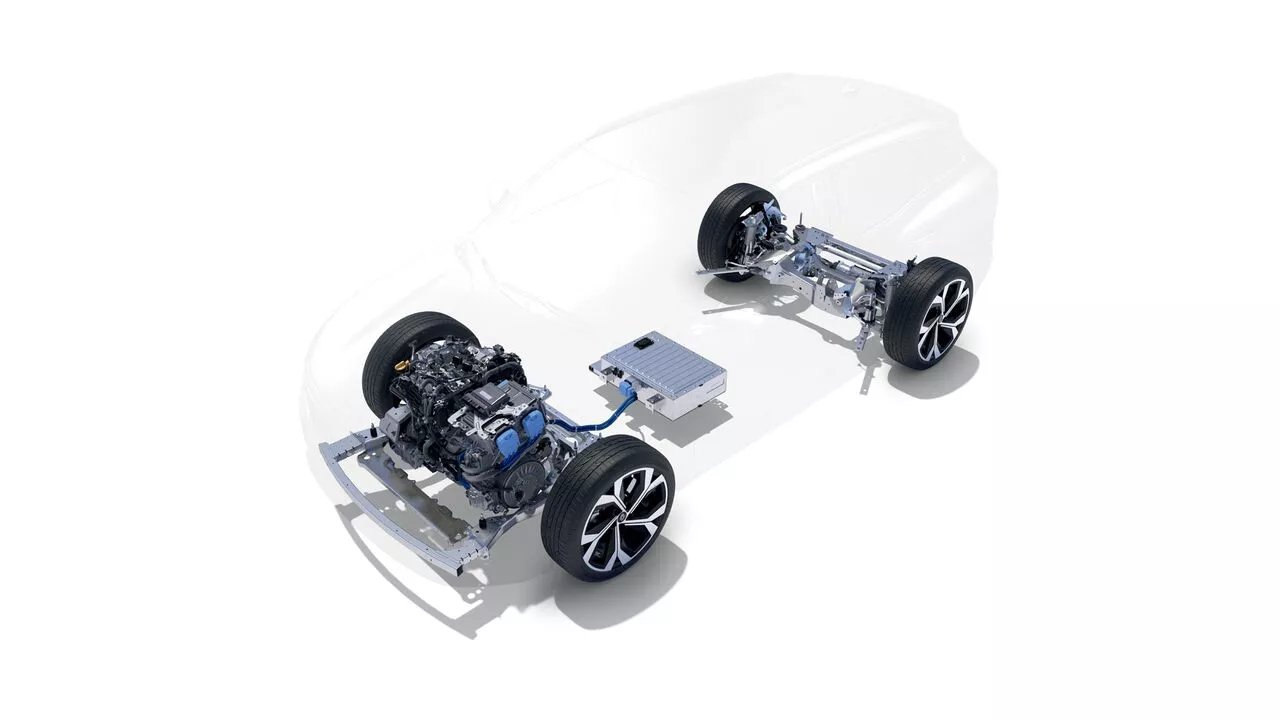
he principle behind E-Tech hybrid technology
Renault made the choice to develop 2 types of technology: E-Tech full hybrid, for vehicles that do not need to be plugged in, and E-Tech plug-in hybrid, for vehicles that can be plugged in. Both options offer environmentally-friendly vehicles that are cost-effective, combining driving pleasure and everyday simplicity.
They operate in the same way, with only 2 differences:
- the size of the battery, and therefore the capacity to drive 100% electric,
- E-Tech plug-in hybrid vehicles can connect to the mains to charge.
our hybrid powertrains
They are called “series-parallel hybrids” because they offer the option of operating as 100% electric, as a hybrid (electric + combustion engine) or with the combustion engine alone.
They have 2 electric motors as well. as a combustion engine.
The innovative technologies integrated into the car (smart gearbox, energy management system, regenerative braking) make it possible to switch between the different powertrains or to operate them simultaneously when necessary. This helps to optimise the vehicle’s performance and consumption.
E-Tech powertrains offer excellent acceleration, dynamic pick-up, and reduced CO2 emissions and fuel consumption.
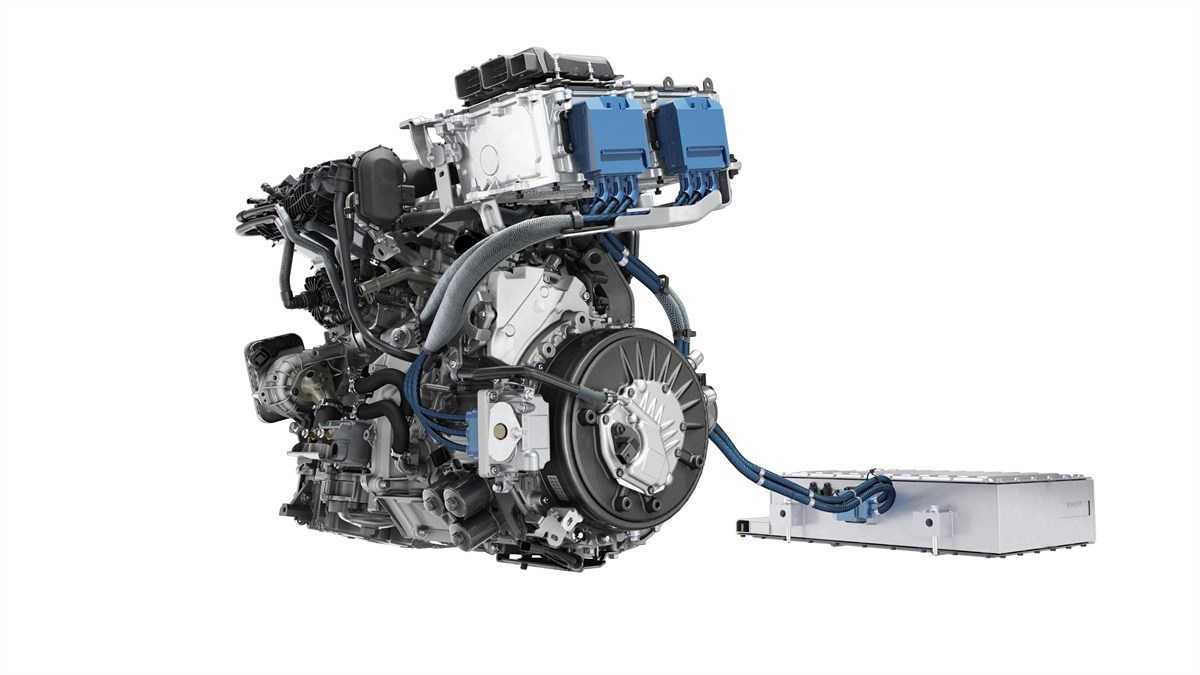

PETROL ENGINE
The combustion engines are specially designed to reduce consumption and CO₂ emissions. Fitted with a particulate filter, they combine economy, efficiency and performance.

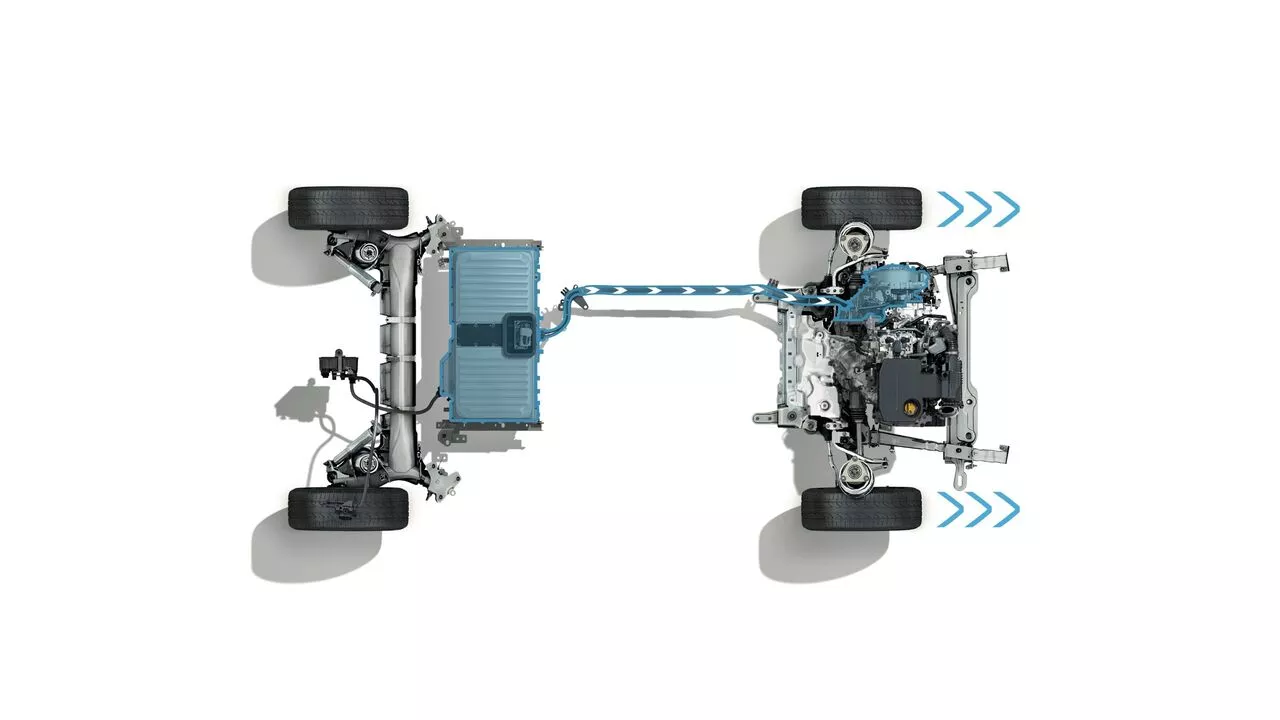
THE TRACTION BATTERY
A battery that stores the energy required to move the vehicle and then keep it running in electric mode. Its size varies greatly depending on the type of powertrain: up to 2 kWh for a full hybrid and up to 10.4 kWh for a plug-in hybrid.
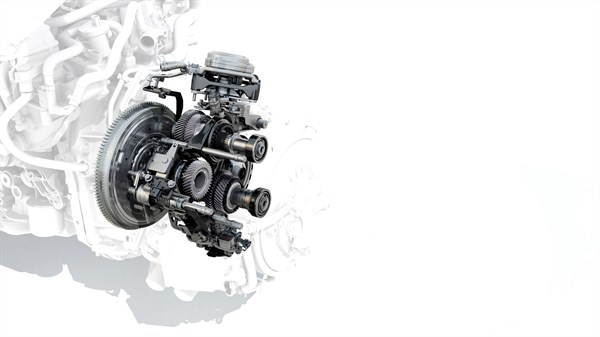
AUTOMATIC INTELLIGENT MULTIMODAL GEARBOX
This revolutionary gearbox delivers optimum performance. It works in combination with the energy management system which draws from the Renault Group’s F1 expertise. In all, it has up to 15 driving modes through 2 electric gears and 4 combustion engine gears, which can work together1 or separately.

MAIN ELECTRIC MOTOR
It helps to start the vehicle, provides 100% electric driving, powers the wheels and recharges the battery when you brake or decelerate.
A SECONDARY ELECTRIC MOTOR
It acts as the starter motor and the high-voltage generator for the battery. It is also used as a stabiliser during gear changes, to avoid judder and vibrations.
POWER ELECTRONICS
The system continuously ensures the transfer and AC/DC conversion of the electrical energy between the traction battery and the electric motor.
the different modes of traction
A hybrid engine is made up of 2 main motors that alternate or operate simultaneously to power the vehicle. Find out about the different modes of traction:
electric traction
At start-up, only the electric motor drives the wheels, therefore no fuel is consumed. Start up silently and drive up to 130 kph for up to 5 minutes using only electric power, depending on your driving style and the model*.
* Austral E-Tech full hybrid 200
hybrid traction
This mode involves the simultaneous use of two power sources to drive the vehicle.
For dynamic driving, the petrol engine backs up the electric motor to maintain performance. The two motors work together to increase the power of your car. This is what is known as parallel hybrid operation.
In some cases, when the battery level is low, the 2 motors operate at the same time, but only the electric motor drives the wheels. In this specific case, the electronic management activates the internal combustion engine to optimise the overall consumption and to recharge the battery. This is what is known as series hybrid operation.
combustion engine traction
When just the combustion engine is running, it is used at its optimal speed, to drive the vehicle’s wheels and to recharge the battery. The vehicle’s overall consumption is optimised and the additional energy is stored to help resume electric driving.
from one mode of traction to another
You can switch from one traction mode to another in two ways:
- automatically, using the onboard electronic management system. This system analyses the battery charge level, the demand for acceleration and the type of road, and adapts the traction mode accordingly, which helps to optimise the vehicle’s performance.
- manually, from the dashboard, only for plug-in hybrids, when choosing to drive 100% electric.
managing charging
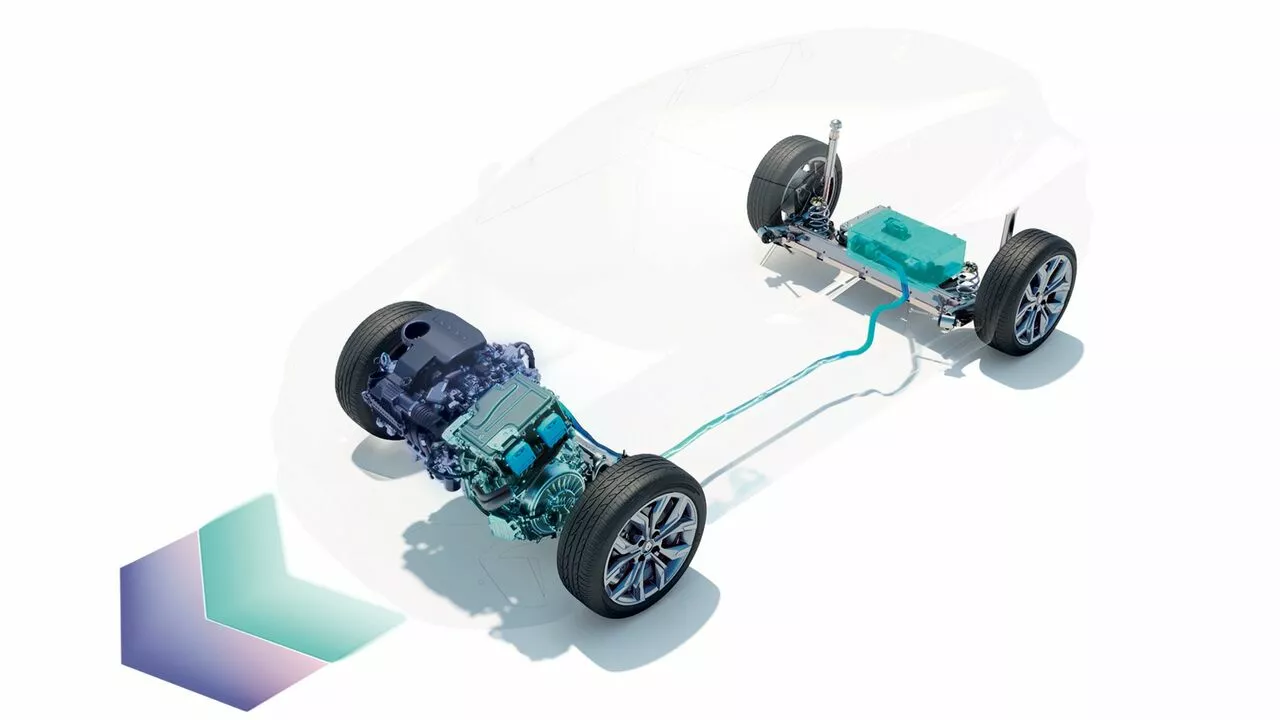
the battery in full hybrid vehicles
charges only when you are driving, using kinetic energy. These vehicles do not need to be plugged in, as they have a system that recovers energy when you brake or decelerate. This is enough to completely recharge the battery.
the battery in plug-in hybrid vehicles
mainly charges by plugging the vehicle into the mains, but also as you drive (around 10% of potential recharging). Plug-in hybrid vehicles have an additional flap that can be used to completely recharge the battery.
the Renault E-Tech full hybrid and E-Tech plug-in hybrid range

E-Tech full hybrid
The vehicles have 2 electric motors and a combustion engine, which recharge as you drive and make it possible to drive 100% electric for up to 80% of the time (WLTP urban cycle).

E-Tech plug-in hybrid
Vehicles with a combustion engine and 2 electric motors with the possibility of recharging their battery, which makes it possible to drive 100% electric for up to 50 km in mixed use (the WLTP cycle corresponding to different types of roads).
your questions on how hybrid cars work
The vehicle manages switching between the electric, hybrid and combustion traction automatically using an electronic system. It takes three criteria into account, to offer the best compromise between performance and consumption:
- the demand for acceleration from the pedal;
- the profile of the road on which you are driving;
- the battery charge level.
Essentially, during start-up, during steady driving and normal acceleration, a hybrid vehicle mostly uses the electric motor. When you push down harder on the accelerator, when the nature of the terrain requires more power (e.g. for a steep climb) or when the battery is not sufficiently charged, the vehicle engages the combustion engine. Depending on the case, the combustion engine will complement the electric motor (hybrid traction) or replace it entirely (combustion engine traction).
No, it’s not possible.
A hybrid car continues to drive, even when the traction battery is depleted, by using the combustion engine. However, the opposite is not true: the hybrid and electric traction modes are there to operate alternately with the combustion mode, but not to replace it entirely. If a hybrid car has run out of petrol, the other modes of traction can only take over briefly before the car stops.
The electric battery is not always used, as the vehicle also operates using the combustion engine. The wear on the battery is therefore gradual and does not provoke a sufficient loss of capacity to prevent the vehicle from operating.
Moreover, if the vehicle is protected from extreme temperatures, particularly the cold, it can last for a hybrid vehicle’s entire life span.
The battery in a Renault hybrid vehicle is guaranteed for 8 years or 160,000 km.


